添加任务
添加任务的功能实现和前面实现用户功能的流程完全一致:
- 根据需求完善模型
- 创建需要的表单
- 编写控制器代码
完善 task 模型
打开 app/model/task.php(如果没有则用 WebSetup 创建),修改下面几个地方:
属性和关联的定义:
'props' => array ( ..... 'is_completed' => array('readonly' => true), 'completed_at' => array('readonly' => true), 'owner' => array(QDB::BELONGS_TO => 'User', 'source_key' => 'owner_id'), ),
验证规则:
'validations' => array ( 'subject' => array ( array('not_empty', '任务主题不能为空'), array('max_length', 180, '任务主题不能超过 60 个汉字或 180 个字符'), ), ),
自动填充规则:
'create_autofill' => array ( // 新建任务的 is_completed 状态总是为 false 'is_completed' => false, // 新建任务的 completed_at 值总是为 null 'completed_at' => null, //自动填充修改和创建时间 'created'=>self::AUTOFILL_TIMESTAMP, 'updated'=>self::AUTOFILL_TIMESTAMP ), 'update_autofill'=>array( 'updated'=>self::AUTOFILL_TIMESTAMP ),
create_autofill 设置可以在创建对象时将指定的数值设置为特定值。例如“新建任务的状态是未完成”这个逻辑就可以通过简单的指定 create_autofill 来实现。
最后再加上安全性设置:
'attr_accessible' => 'subject, description',
attr_accessible 设置会在构造对象时产生作用:
$task = new Task($_POST); $task->save();
上述代码构造了一个新的 task 模型实例,并且以表单的值作为对象初始值。这种方式很方便,但存在一个安全隐患。
假设用户在客户端构造一个包含“task_id”字段值的表单,并提交到服务器,那么此时构造出来的 $task 对象就包含了 task_id 属性值。由于 task_id 属性也是 task 对象存储在 tasks 表中的主键字段,那么在接下来调用 save() 方法时,实际完成的操作不是“新建一个 task 对象”,而是“更新一个已有的 task 对象”。因此我们务必要堵上这样的漏洞。
设置 attr_accessible 选项,可以指定哪些属性可以通过构造函数来赋值,这样上面的代码中即便表单包含 task_id 值,也不会被存入新建的对象,实现了安全性。补充类方法
任务必须通过用户创建,所以需要在用户模型加入对应的类方法/** * 创建任务 * @param string $subject * @param string $description * @return Task */ function createTask($subject,$description){ $task=new Task(array( 'subject'=>$subject, 'description'=>$description )); $task->owner_id=$this->user_id; $task->save(); return $task; }
添加控制器动作
修改 tasks 控制器,添加 actionCreate() 动作方法:
function actionCreate() { if (request_is_post()){ // 通过应用程序对象获得当前用户对象 $user = $this->_app->currentUserObject(); // 通过用户对象创建任务 try { $task = $user->createTask(request('subject'), request('description')); // 保存并重定向浏览器 $task->save(); return $this->_redirect(url('tasks/index')); }catch (Exception $ex){ $this->_view['errors']=$ex->getMessage(); } } }
以及对应的视图 app/view/tasks/create.php:
<?PHP $this->_extends('_layouts/default_layout'); ?> <?PHP $this->_block('contents');?> <div> <form action="" method="post"> <?php if (!empty($errors)):?> <div class="alert"> <?php echo $errors?> </div> <?php endif;?> <fieldset> <legend>添加任务</legend> <p> <label>任务主题</label> <input name="subject"> </p> <p> <label>任务描述</label> <textarea name="description" style="width:400px;height: 100px;"></textarea> </p> <p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </p> </fieldset> </form> </div> <?PHP $this->_endblock();?>
这里我们用到了应用程序对象的一个新方法 currentUserObject()。但这个方法还需要添加到 app/myapp.php 中,代码如下:
/** * 获得当前用户对应的 User 模型对象实例 * * @return User */ function currentUserObject() { $data = $this->currentUser(); if ($data===null){ throw new MyAppException('当前访问用户没有对应的 User 对象'); } $user = User::find('user_id = ?', $data['user_id'])->getOne(); if ($user->isNewRecord()) { return $user; } else { throw new MyAppException('当前访问用户没有对应的 User 对象'); } }
currentUserObject() 方法不但通过查询操作获得 User 模型对象实例,而且通过检查其 ID 来确保这个对象是肯定存在的。这种做法从根本上保证了后续数据的有效性。
保证逻辑的正确性和数据的有效性是应用程序的核心使命!
测试创建任务
通过浏览器访问 http://localhost/app/index.php?controller=tasks&action=create 就可以看到添加任务表单:
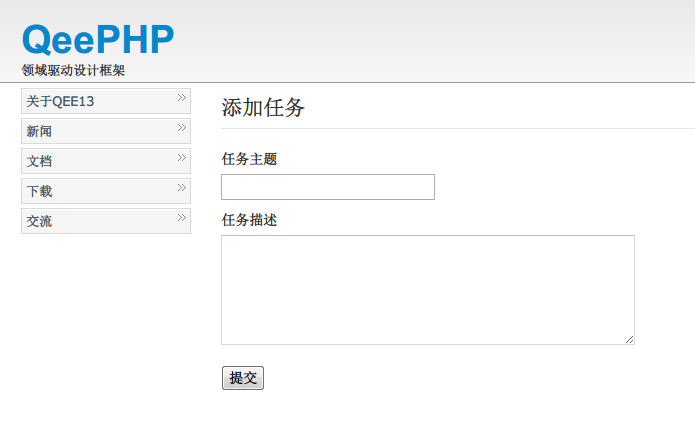
添加任务表单
输入有效数据后提交,可以通过 phpMyAdmin 看到数据已经成功添加:
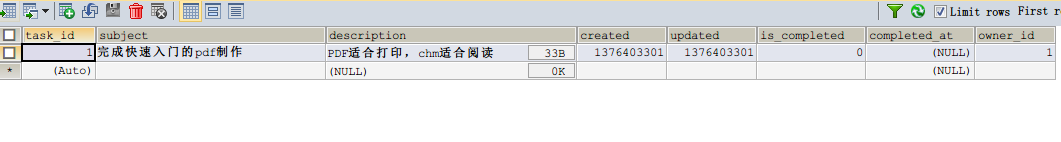
成功保存到数据库的任务数据
添加任务查看页面
修改 tasks 控制器的 actionIndex() 动作方法:
function actionIndex() { $user=$this->_app->currentUserObject(); $tasks=Task::find('owner_id=?',$user->id())->getAll(); $this->_view['tasks']=$tasks; }
以及对应的视图 _code/view/tasks/index.php:
<?PHP $this->_extends('_layouts/default_layout'); ?> <?PHP $this->_block('title');?>我的任务<?PHP $this->_endblock();?> <?PHP $this->_block('contents');?> <div class="tasks"> <h1>我的任务</h1> <?php foreach ($tasks as $task): ?> <h2><a href="<?php echo url('tasks/edit', array('task_id' => $task->id())); ?>"><?php echo h($task->subject); ?></a></h2> <p class="meta"> <?php if ($task->is_completed): ?> <em>已经在 <?php echo date('m-d H:i', $task->completed_at); ?> 完成该任务</em> <?php else: ?> <strong>添加日期:<?php echo date('m-d H:i', $task->created); ?></strong> <?php endif; ?> </p> <?php if ($task->description): ?> <p class="description"> <?php echo nl2br(h($task->description)); ?> </p> <?php endif; ?> <hr /> <?php endforeach; ?> </div> <?PHP $this->_endblock();?>
最后在public/css/base.css 添加一些样式定义,以便让列表页面看上去更美观:
.tasks h2 { font-size: 18px; font-weight: bold; } .tasks p { font-size: 14px; color: #333; font-weight: normal; } .tasks p.meta { font-size: 12px; font-weight: normal; color: #666; }
现在添加任务后就可以看到任务列表了:
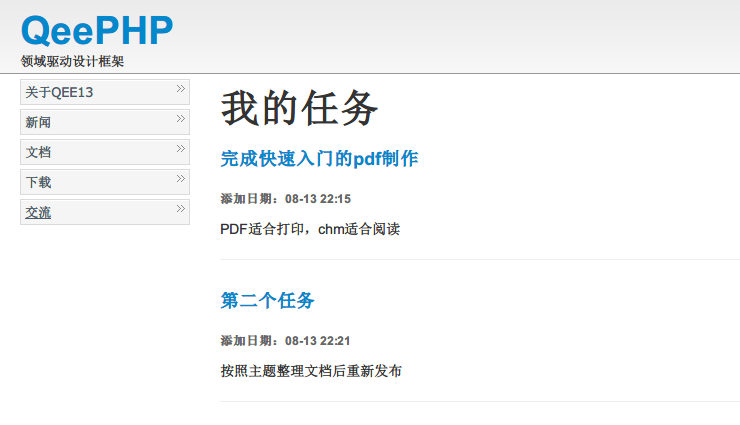
任务列表页面